What is UX Design? Difference between UX and UI Design
If you’ve been wondering about the distinction between UX design and UI design, you’re not alone. Often used interchangeably, they actually describe totally different things. User Experience (UX) design has become a pivotal element in the realm of digital products and services, playing a crucial role in shaping the way individuals interact with technology. Often confused with User Interface (UI) design, UX design encompasses a broader spectrum, focusing on the overall user journey and satisfaction.
In today’s hyper-competitive digital landscape, the success of your online presence hinges on delivering a seamless and captivating user experience (UX) and a visually stunning user interface (UI). At Serve24Hour, we take pride in offering world-class UX and UI design services that transcend geographical boundaries, ensuring your brand resonates with a global audience.
AI Tools for UX and UI Design:
AI has significantly impacted the fields of UX (User Experience) and UI (User Interface) design, introducing various tools and technologies that streamline processes, enhance creativity, and improve overall design efficiency. Here are some AI tools for UX and UI design:
- Adobe Sensei: Adobe Sensei is an artificial intelligence and machine learning platform integrated into Adobe’s Creative Cloud. It offers features like automatic image tagging, content-aware fill, and facial recognition that can be valuable in UX and UI design.
- Sketch2React: Sketch2React is an AI-powered tool that transforms Sketch designs into React code. This can significantly speed up the development process by automatically generating code snippets from design files.
- Framer X: Framer X combines design and code, allowing designers to create interactive UI components using React. The AI-powered features include smart layout suggestions and automatic code generation, making it easier for designers to create responsive interfaces.
- UXPin: UXPin is a collaborative design platform with AI capabilities. It assists in creating design systems, prototyping, and collaborating on design projects. The AI features help automate repetitive tasks and suggest design improvements based on best practices.
- Adobe XD Auto-Animate: Adobe XD, a popular UX/UI design tool, incorporates Auto-Animate, an AI-powered feature that enables automatic animation between artboards. This simplifies the process of creating interactive prototypes and enhances the overall user experience.
- RunwayML: RunwayML is a creative toolkit that enables designers to integrate machine learning models into their designs. It allows for the creation of interactive and dynamic content by leveraging pre-trained models for tasks like image recognition, style transfer, and more.
- Canva: Canva is a user-friendly design tool that utilizes AI to assist users in creating visually appealing designs. It provides suggestions for design elements, layout, and color schemes, making it accessible for users with varying design expertise.
- Miro: Miro is a collaborative online whiteboard platform that incorporates AI to enhance collaboration and ideation in design processes. It aids in creating user journey maps, wireframes, and collaborative design workshops.
- The Grid: The Grid is an AI-powered website design platform that autonomously designs and builds websites based on user preferences and content. While not as widely adopted, it showcases the potential for AI in automating aspects of web design.
- Botsociety: Botsociety is an AI tool focused on conversational design for chatbots and voice interfaces. It allows designers to prototype and simulate conversational experiences, ensuring a user-friendly and intuitive interaction.
Difference between UX and UI Design
UX design focuses on creating a consistent and meaningful user experience by understanding user needs, conducting research, and designing intuitive interfaces, while UI design focuses on the visual, interactive components of a product to create aesthetically-pleasing interfaces.
UX vs. UI design:
UX design refers to the expression “user experience design”, while UI design means “user interface design”. Both components are crucial to a product and work closely together. Yet, regardless of their professional relationship, the roles themselves are quite different, referring to very different aspects of the product development process and the design discipline.
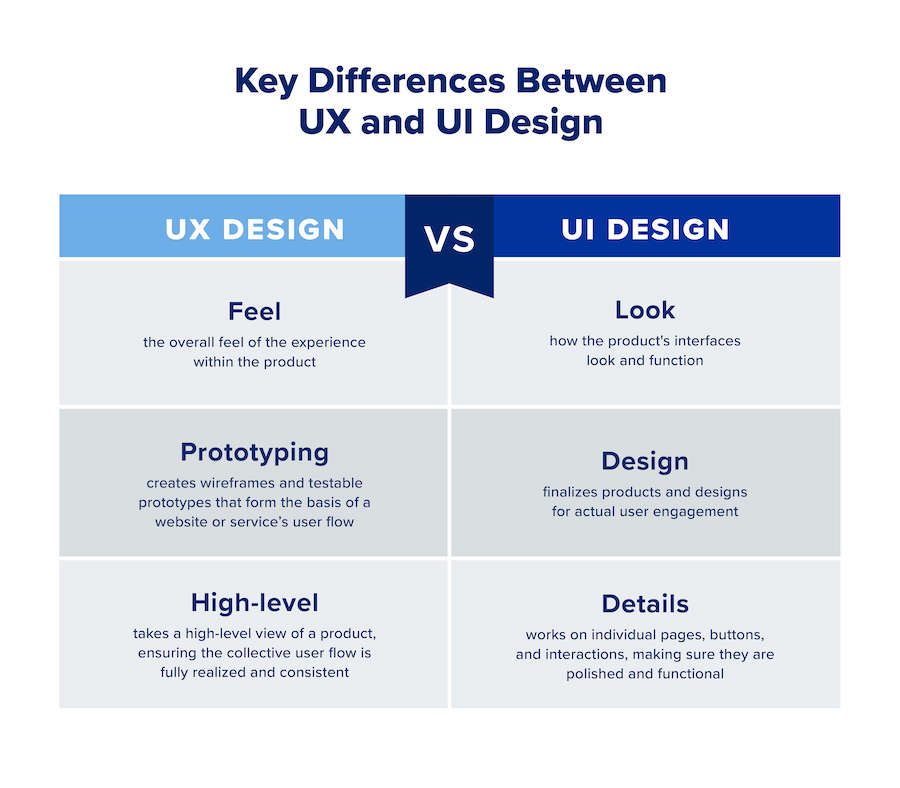
What is user experience (UX) design?
There’s something else to UX design than meets the eye on a user interface. The UX design process includes market research, wireframe development, prototype testing, and cross-functional collaboration. There are five essential steps to effective UX design:
User Research:
To convey a positive client experience, UX designers need to understand their target audience. Through UX research, they find what their users like, what problems and pain points they’re facing and the way that they act online or while using an app or software. UX designers may likewise perform competitor analysis using a SWOT analysis template to define their product niche.
Information architecture:
When UX designers understand users’ needs and behaviors, they can create information architecture (IA) for their product or site. Designers use IA as a visual blueprint, outlining essential navigation, content order, features, and interactions. One key IA tool is a flowchart layout, which designers use to map out key user flows and decision points.
Wireframing and Prototyping:
Wireframes and prototypes are visual representations of the product’s structure and functionality. They allow designers to test and refine ideas before moving on to the actual development phase. Serve24Hour’s online prototypes facilitate collaboration among designers, developers, and product owners, bringing everyone together to produce a more responsive, accessible, usable, and engaging end product.
Testing and troubleshooting:
Product mockup tools created by Serve24Hour’s community of professional designers help UX designers, developers, and product owners see how features will work in practice. If testing reveals issues like confusing navigation, menus, or forms, the team can change them before launch.
Ongoing updates:
Even after a digital product has entered the market, a UX designer’s job is rarely genuinely finished. With new user feedback and back-end analytics, they can design refreshes and improvements. For example, analytics may reveal that an online business checkout process is too long, leading to a high cart abandonment rate. To resolve this issue, UX designers may streamline some checkout steps.
4 key UI design considerations:
To make connecting with UI, designers consider these four key elements:
- Page layout: Preferably, the organization of a web page or mobile app screen should seem intuitive to users. However, to organize it that way, UI designers have to make dozens of well-considered decisions—from the header position to the amount of white space.
- Color scheme and font selection: UI designers carefully pick the colors and fonts on a digital product interface for consistency, accessibility, and brand alignment.
- Interactive elements: From button design to drop-down menus, UI designers style digital product screens to make client flows intuitive.
- Wireframe and prototype fidelity: UX designers frequently set up basic wireframes and prototypes. UI designers can assist transform them into high-fidelity, functional, interactive product mockups.
Conclusion:
In essence, UX design and UI design are intertwined but serve different purposes in the creation of digital products. While UI design is concerned with the visual aesthetics, UX design encompasses the entire user journey, ensuring a seamless and delightful experience. A successful product combines both UX and UI elements to deliver a holistic and user-centric solution. As technology continues to evolve, the importance of UX design in crafting meaningful and engaging user experiences will only continue to grow.
